스포트라이트
Agronomist, Arboriculture Researcher, Crop Nutrition Scientist, Forage Physiologist, Horticulture Specialist, Plant Physiologist, Plant Research Geneticist, Research Scientist, Research Soil Scientist, Scientist
“Plants are vital to all life on Earth,” says the Smithsonian Institute. They not only remove carbon dioxide from the air we breathe, they literally produce oxygen, too! If that weren’t enough, nutrient-rich plants are the primary food source for most living things—including humans, who cultivate crops and consume their edible parts (i.e., vegetables). We also rely on seed-bearing plants which produce tasty fruits!
Plant Scientists and Botanists study our world’s treasure trove of plants and ensure they’re well taken care of. From critical farm crops like corn, wheat, barley, and potatoes to plants we use for medicines or ornamentation, all these plants have unique needs related to the amount of sun and water they get and the type of soil they grow in. Workers must also identify and control pests, diseases, fungi, and other hazards to each plant type.
Botanists focus more on classification, genetics, and ecology, while Plant Scientists prioritize cultivation, breeding, and disease management. Other related job titles include agronomists, horticulturists, plant pathologists, plant geneticists, and arboriculture researchers.
- Protecting plants and related ecosystems
- Ensuring human populations have enough crops to eat and plants for medicinal purposes
- 커뮤니티의 신체 건강과 복지에 미치는 영향
- Flexibility and variety of work that is available
근무 일정
- Plant Scientists and Botanists work full-time jobs with nights, weekends, and holidays off. However, overtime may be needed to meet deadlines or during emergencies. Travel for fieldwork and site visits to farms or research stations may be needed, so there could be exposure to inclement weather or hazards such as pests or chemicals.
일반적인 의무
- Research better ways for planting, spraying, cultivating, and harvesting plants
- Assess the effects of climate and soil conditions on crops
- Run tests and experiments to find safe methods of storing and moving plants
- Develop ways to boost crop quality and yields
- Understand pests, pesticides, plant diseases, fungi, and their effects on ecosystems
- Classify pests; assist with pest control methods and means
- Determine which insects may be useful, such as pollinators like bees and butterflies, or pest-eating bugs such as ladybugs and tiger beetles
- Find methods to enhance soil, improve disease resistance, and control weeds
- Review findings with employers, stakeholders, governmental agencies, etc.
- Make recommendations to farmers about land usage and problem avoidance, such as mitigating erosion
- Investigate problems such as poor growth; try to determine root causes like lack of nutrients in the soil or tainted water supplies
- Examine how soil changes under various natural or manmade circumstances. Look for ways to amend or alternate soils to boost productivity
- Develop and help implement sustainable farming methods
- Conduct fieldwork and site visits to take soil samples, monitor situations, and look for hazards
- Collect data from site sensors; compile data using software and analyze results
- Look for signs of pollutants and environmental changes that impact plants
- Collaborate with appropriate governmental agencies when reporting pollution activities
- Survey lands for classification and planning purposes
- Research requirements for urban green spaces
- Supervise land conservation/reclamation projects
- Research plants to use for green fuels
추가 책임
- Stay up-to-date on crop/plant-related regulations, standards, and challenges
- Write and publish papers for peer-reviewed journals
- Offer advice regarding environmental management and conservation
- Submit records and technical reports to local, state, or federal agencies
- 공공 교육 및 인식 개선 프로그램 지원
- 장비 교정, 샘플 추적, 데이터 입력, 실험실과의 협업
소프트 스킬
- 능동적 학습
- 활동 조정
- 분석
- 세부 사항에주의
- 의사소통 기술
- 비판적 사고
- 결정적인
- 디테일 지향
- 독립의
- 조사의
- 모니터링
- 목표
- 조직
- 통찰력
- 고집
- 문제 해결
- Reasoning
- 안전 지향
기술 능력
- Analytical Chemistry
- Botanical knowledge
- Data visualization programs
- Environmental monitoring tools
- 지역, 주, 연방 수질 규정 숙지
- Fieldwork, sampling, and lab techniques
- First aid
- Genomics and bioinformatics
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and remote sensing tools
- ImageJ image analysis software
- 마틀랩
- Microbiology and molecular biology
- 개인 보호 장비 사용
- Plant breeding and genetics, physiology and biochemistry, propagation, cultivation, and pathology
- Programming languages like R and Python
- Safety protocols working around pests, pesticides, and chemicals
- Scientific writing
- 통계 분석
- Biotechnology companies
- 식물원
- 교육 기관
- Horticulture businesses
- 실험실
- Nurseries
- 지방, 주 및 연방 정부 기관
- Pest management companies
We rely on Plant Scientists and Botanists to conduct diligent research that enhances our understanding of plant biology, ecology, and agriculture. Through their tests, experiments, and findings, society can benefit from better agricultural practices, enhanced plant traits, and more sustainable solutions for food security and environmental challenges. Without their hard work, we could face crop shortages or ecological nightmares.
The responsibilities are huge, but workers often serve as part of larger interdisciplinary teams! They must sometimes get out in the field to conduct assessments and gather samples, so expect regular travel and exposure to inclement weather or other environmental conditions. In addition, there may be potential for exposure to pests, pesticides, and chemicals, so it is important to wear appropriate protective gear like gloves, goggles, or face masks.
There are several trends in the plant science industry right now, with three of the most important being precision agriculture, the demand for more plant-based foods, and the need for climate-resilient crops.
Precision agriculture relies on high-tech, data-driven approaches to optimize agricultural practices. Sensors, drones, GPS technology, and data analytics all play a part in this new wave of smart farming, which lets farmers tailor irrigation, fertilization, and pest control to improve yields and reduce waste and environmental impacts!
The demand for plant-based foods has risen thanks to health and environmental concerns, not to mention many consumers just don’t want to eat meat anymore. Plant Scientists are hard at work developing ways to improve plant-based alternatives to meat-based products. They are also striving to enhance climate-resilient crop varieties, breeding plants that can tolerate extreme temperatures, drought, flooding, and other environmental stresses.
Plant Scientists and Botanists are often very patient and probably always loved working in the garden, getting their hands in the soil. They care about plants and the important benefits they contribute to our fragile ecosystems. They’re also analytical and likely excelled in STEM subjects from an early age, and liked being able to apply science concepts in practical ways.
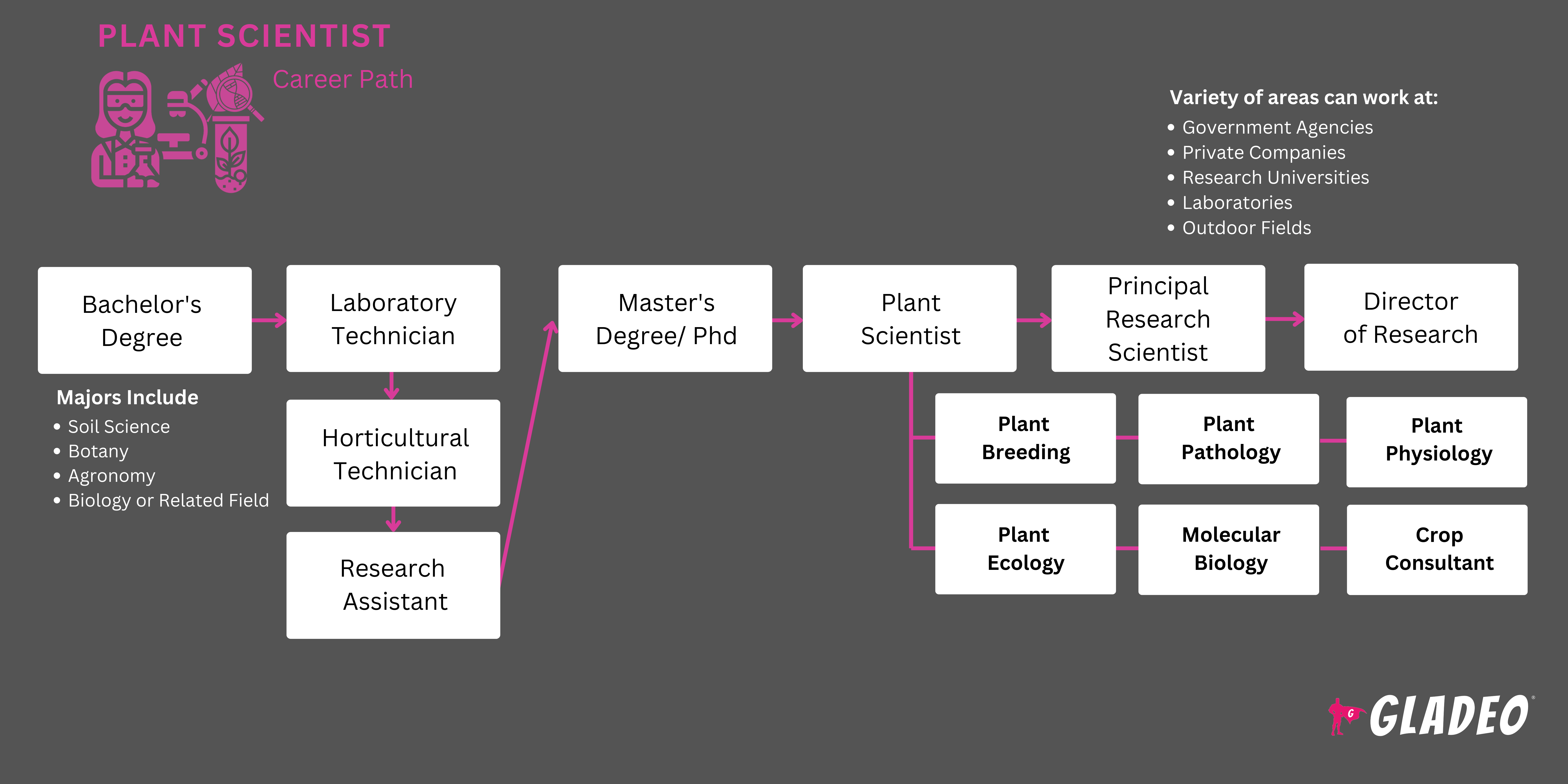
- Plant Scientists and Botanists generally need a bachelor’s with a major in plant science, plant biology, botany, horticulture, agricultural science, viticulture and enology, or a related field
- A master’s in plant science may not be needed but can make you more competitive and may qualify you for a higher starting salary or position
- Per CareerOneStop, 60% of Plant Scientists have a bachelor’s, 27% have a master’s, and 13% have a doctorate
- 일부 학생들은 시간과 비용을 절약할 수 있는 학사/석사 복수 학위 과정을 선택하기도 합니다.
- An internship can develop practical skills. Study abroad opportunities are another way to expand your learning outcomes!
- 일반적인 대학 과정 주제는 다음과 같습니다:
- Horticulture
- Plant biology
- Plant breeding and genetics
- Plant pathology and plant-microbe biology
- Soil and crop sciences
- Students in some programs will need to select an area of concentration, such as:
- Ecology of Managed Landscapes
- Organic Agriculture
- Plant Breeding & Genetics
- Plant Pathology & Plant-Microbe Biology
- Soil Science
- 선택적 인증에는 다음이 포함됩니다.
- Associate Professional Horticulturist
- Certified Crop Adviser - Resistance Management Specialty
- Certified Crop Adviser - Sustainability Specialty
- Certified Professional Agronomist
- Accredited Agricultural Consultant
- Associate Certified Entomologist
- Tree Risk Assessment Qualification
- Wetland Professional in Training
- Associate Professional Soil Scientist
- Students should seek colleges offering majors in plant science, plant biology, botany, horticulture, agricultural science, or a related field
- 인턴십 또는 실무 경험을 쌓을 수 있는 기회를 제공하는 프로그램을 찾아보세요.
- 수업료 및 수수료 비용을 비교하여 주 내 비용과 타주 비용에 주목하세요.
- 장학금 및 재정 지원 옵션 검토
- 졸업생을 채용하는 회사와 파트너십을 맺은 프로그램이 있는지 확인하세요!
- 졸업생에 대한 졸업 및 취업 통계 기록하기
- Sign up for high school classes in biology, chemistry, math, environmental studies, Earth science, physics, geology, ecology, statistics, and writing. Consider doing advanced placement classes if possible
- You’ll need a strong math and science foundation, plus experience with computer programs and laboratory work! Get some scientific research and lab experience under your belt, any way you can
- Start your own garden at home or at a community plot
- Look for internships, cooperative experiences, part-time jobs, or volunteer projects while in college. You could work at a plant nursery, on a farm, or for a local college.
- Ask a teacher or counselor about school-related plant or agricultural programs you can participate in. Also, participate in extracurricular activities where you can manage projects and work with teams
- Read books and articles and watch YouTube channels about plant science and botany. Get in the habit of reading technical materials such as scientific papers, and not just blogs
- Take ad hoc courses via Coursera, Class Central, and other sites
- Request an informational interview with a working Plant Scientist or Botanist in your community
- 전문가 단체에 가입하여 배우고, 공유하고, 친구를 사귀고, 네트워크를 확장하세요( 리소스 > 웹사이트 목록 참조).
- 나중에 추천인 역할을 할 수 있는 사람의 이름과 연락처 정보를 기록해 두세요.
- Check out job portals like Indeed.com, LinkedIn, Glassdoor, Monster, CareerBuilder, SimplyHired, ZipRecruiter, USAJOBS, AgCareers.com, Greenhouse Grower, Society for Experimental Biology’s job board, American Society of Plant Biologists’ job board, and the websites of local colleges or universities
- Look on Craigslist for local opportunities with smaller employers
- 경험을 쌓아 승진할 수 있도록 초급 직책을 수락할 준비를 하세요.
- 채용 공고의 중요한 키워드를 메모해 두세요. 이력서 및 자기소개서에 해당 키워드를 활용하세요.
- Check out Plant Scientist and Botanist resume examples and search online for sample interview questions
- 전문가 네트워크의 모든 사람에게 구직 중임을 알립니다.
- 더 많은 일자리가 있는 곳으로 이직 고려하기
- The states with the highest employment numbers for Soil and Plant Scientists are North Carolina, Iowa, Washington, Nebraska, and Michigan
- The states with the highest concentration of jobs are North Dakota, Iowa, South Dakota, Nebraska, and Montana
- The states that pay the most for these jobs are Washington D.C., Louisiana, Maryland, Alabama, and Mississippi
- 대학 교수, 전 상사 및/또는 동료에게 개인 추천인이 되어 줄 의향이 있는지 물어보세요. 사전 허가 없이 개인 연락처 정보를 제공하지 마세요.
- 학교 커리어 센터나 친구들과 함께 모의 면접을 해두면 실제 면접에 대비하고 더 편안하게 임할 수 있습니다.
- 면접에 적합한 복장을 갖추고 해당 분야에 대한 열정과 지식을 보여주세요.
- 현재 업무에 최선을 다해 고품질의 작업을 제시간에 제공하세요.
- 상사에게 추가 책임을 맡고 싶고 필요에 따라 추가 교육을 받을 의향이 있음을 알리세요. 승진 기준을 확실히 이해하세요.
- Keep up with environmental trends and challenges that impact soil and plants, especially vital crops
- 평생 교육 과정, 워크샵 또는 컨퍼런스를 통해 새로운 기술에 대해 알아보세요.
- 독립성, 성실성, 리더십을 보여주세요. 동료들과 대화하며 정보와 팁을 교환하세요. 다른 사람을 가르치고 멘토링하기
- Stay on top of the latest software developments, and master programs or languages like R, Python, MATLAB, ImageJ, plant genome databases, etc.
- Participate in professional organizations like the American Society of Agronomy. Go to conferences and workshops. Give lectures. Keep learning and expanding your knowledge base and skills
- 팀원들과 효과적으로 협업하고 지역 환경 기관과 긴밀한 관계를 구축하세요.
- Knock out a specialty certification such as the American Society of Farm Managers and Rural Appraisers’ Accredited Agricultural Consultant cert
- Publish papers in high-impact journals to demonstrate your research skills and to get your work seen by a wider audience
- Complete a graduate degree and consider specializing in a hard-to-fill niche. Currently, there’s a need for experts in plant breeding, plant pathology, soil science, environmental plant science, and molecular plant biology
- 사내 채용 공고를 눈여겨보세요! 경력 목표에 맞는 직무에 지원하세요
웹사이트
- AgCareers.com
- 미국 과학 진흥 협회
- 미국 지구 물리학 연합
- American Phytopathological Society
- 미국 원예 과학 협회
- 미국 미생물학 학회
- 미국 농경학 협회
- 미국 식물 생물학자 협회
- ASA/CSSA/SSSA
- BASF
- 미국 식물학회
- 질병 통제 센터
- 미국 작물 과학 협회
- 농무부
- 다우 아그로사이언스
- 미국 생태 학회
- 미국 곤충 학회
- 환경 보호국
- 산림청
- 유해물질관리연구소
- 국제 침식 제어 협회
- 미국 진균 학회
- 국립 환경 보건 협회
- 국립 식품 농업 연구소
- 국립 보건원
- 국립 공원 서비스
- 자연 보호 단체
- 식물성 식품 협회
- 선충 학회
- 신젠타
- 국립 과학 아카데미
- 미국 식품의약국
- USDA 동물 및 식물 건강 검사 서비스
책
- A Gardener's Guide to Botany: The biology behind the plants you love, how they grow, and what they need, by Scott Zona
- How Plants Work: The Science Behind the Amazing Things Plants Do, by Linda Chalker-Scott
- Plant Science: Growth, Development, and Utilization of Cultivated Plants, by Margaret McMahon
- The Science of Plants: Inside Their Secret World, by DK
Most Plant Scientists and Botanists express satisfaction with their careers, but of course, not everyone wants to work in these fields. Some may want more money; others might want more job opportunities in the area where they live. Many towns and cities simply don’t have a lot of openings for Plant Scientists and Botanists.
If you’re interested in related career options, consider the below similar occupations:
- 농업 및 식품 과학 기술자
- 농업 엔지니어
- 생화학자 및 생물물리학자
- 생물학자
- 화학 기술자
- 보존 과학자 및 산림 관리인
- 환경 과학자 및 전문가
- 농부, 목장주 및 농업 관리자
- 산업 생태학자
- 미생물 학자
- 정밀 농업 기술자
- 수의사
- 동물학자 및 야생동물 생물학자
뉴스 피드
주요 채용 정보

온라인 과정 및 도구

연봉 기대치
신입 직원의 초봉은 약 $88,000입니다. 중간 급여는 연간 $97,000입니다. 고도로 숙련된 근로자는 약 112,000달러를 받을 수 있습니다.
연봉 기대치
신입 직원의 초봉은 약 8만 5천 달러입니다. 중간 급여는 연간 12만 달러입니다. 고도로 숙련된 근로자는 약 $138,000를 받을 수 있습니다.
연봉 기대치
신입 직원의 초봉은 약 7만 달러입니다. 중간 급여는 연간 9만 달러입니다. 고도로 숙련된 근로자는 약 $114,000를 받을 수 있습니다.
연봉 기대치
신입 직원의 초봉은 약 6만 5천 달러입니다. 중간 급여는 연간 $92,000입니다. 고도로 숙련된 근로자는 약 11만 7천 달러를 벌 수 있습니다.
연봉 기대치
신입 직원의 초봉은 약 8만 4천 달러입니다. 중간 급여는 연간 $97,000입니다. 고도로 숙련된 근로자는 약 119,000달러를 받을 수 있습니다.






